BUG: some (not all) corner-joined polygons are lost after applying either the dissolve() or the buffer(0) methods
See original GitHub issue-
I have checked that this issue has not already been reported.
-
I have confirmed this bug exists on the latest version of geopandas.
-
(optional) I have confirmed this bug exists on the master branch of geopandas.
Note: Please read this guide detailing how to provide the necessary information for us to reproduce your bug.
Code Sample, a copy-pastable example
import rasterio # version 1.2.6
from rasterio.features import shapes
import geopandas as gpd # version 0.9.0
BASEDIR = '/path/to/folder/where/original_raster_is/' # change me!
SRS = 2056 # or whatever SRS you'd like
# Simulate a random binary raster:
N = np.random.randint(2, size=(64,64))
N[50:,54:] = -99999
N = N.astype(np.float32)
results = ({'properties': {'raster_value': v}, 'geometry': s}
for i, (s,v) in enumerate(shapes(N))
)
geometries = list(results)
gdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame.from_features(geometries)
gdf.set_crs(crs=f'epsg:{SRS}',inplace=True)
gdf.to_file(os.path.join(BASEDIR,'gdf.gpkg'), driver='GPKG') # image 1 - original gdf
# %%
# Up to this point, everything is perfectly fine
exported_1 = gdf[gdf['raster_value']==1] # export only polygons which have a value of 1
exported_1.to_file(os.path.join(BASEDIR,'exported_1.gpkg'), driver='GPKG') # image 2 - exported_1
# %%
# From here, there are invalid geometries:
exported_1.is_valid.all() # False
invalids = exported_1[~exported_1.is_valid]
idx = exported_1[~exported_1.is_valid].index
# If I want to dissolve the exported_1 geodataframe:
dissolved = exported_1.dissolve()
dissolved.is_valid.all() # True
dissolved.to_file(os.path.join(BASEDIR,'dissolved.gpkg'), driver='GPKG') # image 3 - dissolved
# There is a problem, some polygons are missing... but there are no more invalid geometries.
# Let's also try the .buffer(0) trick just in case:
cleaned = exported_1.buffer(0) # this cleans the invalid geometries
cleaned.is_valid.all() # True
cleaned.to_file(os.path.join(BASEDIR,'cleaned.gpkg'), driver='GPKG') # image 4 - cleaned
# Same problem: some polygons are missing
Problem description
I have raster file (GeoTIFF) having values of either 0 or 1. This is the result of a viewshed analysis from an observer point relative to a DEM. 1 means the cell of the DEM is “visible”, and 0 means it’s “invisible” from the observer point.
In order to run some vector computations, for storage and sharing reasons, I have vectorized this result using rasterio.
I only need to keep polygons which depict visible regions (value of 1) and I need them all as a single multipolygon, so I have to dissolve them.
When I export the original gdf every polygons are present.
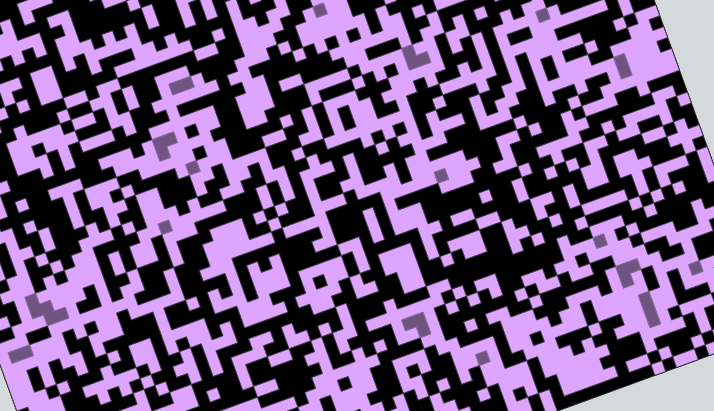
When I export the dissolved or the cleaned geodataframe; some polygons are lost. They are all “corner-joined” black regions, which disappeared, probably “closed” (morphologicaly speaking) by either the dissolve operation or the buffer(0) (both methods seems to give the exact same result), as if they were randomly picking one of the two shape sharing a common corner… This apparent randomness may be related to the ‘orientation’ of such pieces if that makes sense.
More detailed info here: https://gis.stackexchange.com/questions/403523/wrong-features-when-exporting-vectorized-raster-data-to-a-file-using-geopandas-a
image 1 - original gdf:
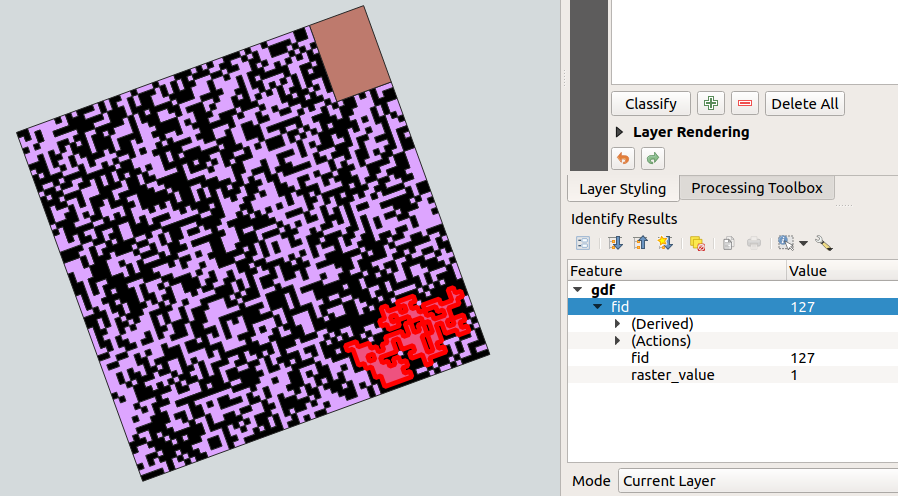
Image 2 - exported_1:
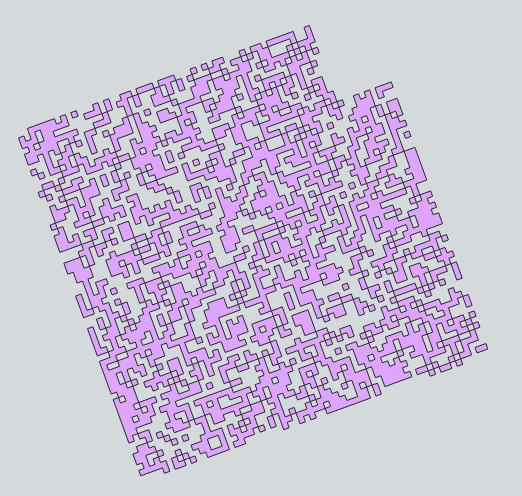
Image 3 - dissolved:
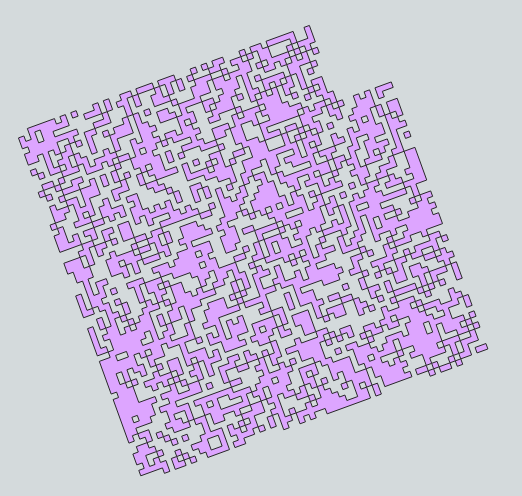
Image 4 - cleaned:
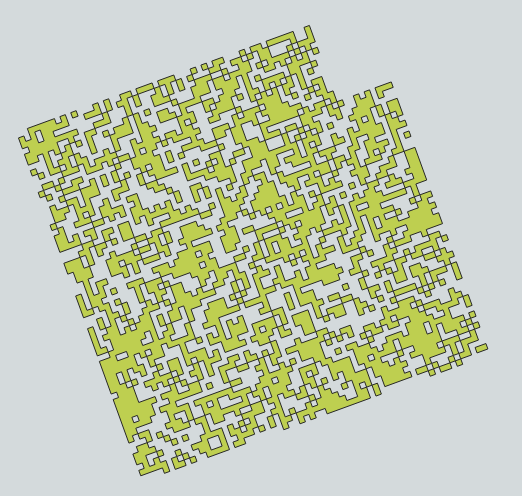
Image 5 - adding transparency on the dissolvedgdf with the original gdf in the background makes the missing polygons appear as darker (deeper) purple regions:

All images are screenshots from QGIS 3.16 after having loaded the exported https://github.com/opengeospatial/geopackage.
Expected Output
A result keeping the original shapes in the first gdf, which also matches the original raster cells, after either applying dissolve() or buffer(0), the former being privileged because I do need a unique multipolygon.
Output of geopandas.show_versions()
SYSTEM INFO
python : 3.6.9 (default, Jan 26 2021, 15:33:00) [GCC 8.4.0] executable : /usr/bin/python3.6 machine : Linux-5.4.0-77-generic-x86_64-with-Ubuntu-18.04-bionic
GEOS, GDAL, PROJ INFO
GEOS : 3.7.1 GEOS lib : /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgeos_c.so GDAL : 3.3.0 GDAL data dir: /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/fiona/gdal_data PROJ : 7.2.0 PROJ data dir: /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/pyproj/proj_dir/share/proj
PYTHON DEPENDENCIES
geopandas : 0.9.0 pandas : 1.1.5 fiona : 1.8.20 numpy : 1.19.5 shapely : 1.7.1 rtree : 0.9.3 pyproj : 3.0.0.post1 matplotlib : 3.3.4 mapclassify: 2.4.2 geopy : 1.21.0 psycopg2 : 2.9.1 (dt dec pq3 ext lo64) geoalchemy2: 0.9.2 pyarrow : None pygeos : None
Issue Analytics
- State:
- Created 2 years ago
- Comments:7 (4 by maintainers)

 Top Related StackOverflow Question
Top Related StackOverflow Question
The issue seems to has been fixed by
rasterio==1.2.8! (which probably relies on the new GDAL 3.3.2…)My GeoPandas’ version (0.9.0) has not changed in between, but I noticed after having upgraded only
rasteriofrom1.2.6to1.2.8that the geometries are now valid!\o/
Update: I’ve tested what is proposed on the GDAL issue at OSGeo/gdal#1158 and indeed, since a week, with the version 3.3.2 of GDAL the geometry has become valid now (thanks @ GDAL devs).
With
gdal_polygonize.pyfrom GDAL 3.3.0:With
gdal_polygonize.pyfrom GDAL 3.3.2: