memory and writing issue during stitching of large images
See original GitHub issueHello @jcupitt ,
I have written a code for mosaicing large number of images. I have used merge function to join the images. I am facing tow issue while saving the result.
- It’s taking lots of RAM (>16GB) in saving the final result, even if I have only 4X156 images.
- I am getting an error while saving the result. Error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "merge_2.py", line 337, in <module>
result.write_to_file('result.tif')
File "/home/lab/.virtualenvs/project/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pyvips/vimage.py", line 481, in write_to_file
), **kwargs)
File "/home/lab/.virtualenvs/project/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pyvips/voperation.py", line 188, in call
raise Error('unable to call {0}'.format(operation_name))
pyvips.error.Error: unable to call VipsForeignSaveTiffFile
TIFFSetField: result.tif: Unknown tag 317
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
VipsJpeg: out of order read at line 640
Code:
from os import listdir,remove
from os.path import isfile, join
import re
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pyvips
import time
def connect(img,r_overlap,c_overlap):
#########################################
# Used for finding information in image #
#########################################
print " connect function : finding regional information"
r=img.shape[0]
c=img.shape[1]
r_overlap,c_overlap=int(round(r_overlap)),int(round(c_overlap))
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
lower_red = np.array([20,20,20])
upper_red = np.array([200,200,200])
mask = cv2.inRange(hsv, lower_red, upper_red)
img=mask
white_space=np.sum(img)/(r*c)
right_connectivity=img[:,c-c_overlap:]
right_score=np.sum(right_connectivity)/(r*c_overlap)
left_connectivity=img[:,:c_overlap]
left_score=np.sum(left_connectivity)/(r*c_overlap)
bottom_connectivity=img[r-r_overlap:,:]
bottom_score=np.sum(bottom_connectivity)/(r_overlap*c)
up_connectivity=img[:r_overlap,:]
up_score=np.sum(up_connectivity)/(r_overlap*c)
right,left,up,bottom=0,0,0,0
white=1
if right_score>0.5:
right=1
if bottom_score>0.5:
bottom=1
if left_score>0.5:
left=1
if up_score>0.5:
up=1
if white_space<0.5:
white=0
score={'white_space':white,'right_score':right,'left_score':left,'bottom_score':bottom_score,'up_score':up}
return score
def vips_image(img):
###########################
# vips to numpy converter #
###########################
format_to_dtype = {
'uchar': np.uint8,
'char': np.int8,
'ushort': np.uint16,
'short': np.int16,
'uint': np.uint32,
'int': np.int32,
'float': np.float32,
'double': np.float64,
'complex': np.complex64,
'dpcomplex': np.complex128,
}
# img = pyvips.Image.new_from_file(sys.argv[1], access='sequential')
np_3d = np.ndarray(buffer=img.write_to_memory(),
dtype=format_to_dtype[img.format],
shape=[img.height, img.width, img.bands])
return np_3d
def warpImages(img1, img2, H):
###############################
# warp image using homography #
###############################
print "warpImages function : finding coordinates"
h1,w1 = img1.shape[:2]
h2,w2 = img2.shape[:2]
pts1 = np.float32([[0,0],[0,h1],[w1,h1],[w1,0]]).reshape(-1,1,2)
pts2 = np.float32([[0,0],[0,h2],[w2,h2],[w2,0]]).reshape(-1,1,2)
pts2_ = cv2.perspectiveTransform(pts2, H)
x_pts2_=pts2_[0][0]
y_pts2_=pts2_[2][0]
pts = np.concatenate((pts1, pts2_), axis=0)
[xmin, ymin] = np.int32(pts.min(axis=0).ravel() - 0.5)
[xmax, ymax] = np.int32(pts.max(axis=0).ravel() + 0.5)
t = [-xmin,-ymin]
Ht = np.array([[1,0,t[0]],[0,1,t[1]],[0,0,1]]) # translation matrixfor negative co-ordinates
H1=np.dot(Ht,H) #getting modified homography matrix
t_pts=np.dot(H1,[img2.shape[1],img2.shape[0],1])
axis=[int(t_pts[0]-img2.shape[1]),int(t_pts[1]-img2.shape[0])]
warped=np.zeros((ymax-ymin,xmax-xmin,3),img2.dtype)
warped[axis[1]:h2+axis[1],axis[0]:w2+axis[0]] = img2
warped[t[1]:h1+t[1],t[0]:w1+t[0]] = img1
return warped,[t[1],h1+t[1],t[0],w1+t[0]],[axis[1],h2+axis[1],axis[0],w2+axis[0]]
def Stitch(imageA,imageB,fx,switch):
#############################
# stitching images in a row #
#############################
print " rowStitch function : finding homography"
res_max=-1
xA1=-1
yA1=-1
intervalx=16
intervaly=16
print "grid size x:%i y:%i"%(intervalx,intervaly)
temp=imageB[:,:int(imageB.shape[1]*0.25)] #temp
if switch==1:
temp = cv2.Laplacian(temp,cv2.CV_32F)
print "laplacian filter in use"
if switch==0:
sobelx = cv2.Sobel(temp,cv2.CV_32F,1,0,ksize=11)
sobely = cv2.Sobel(temp,cv2.CV_32F,0,1,ksize=11)
temp=sobelx+sobely # to get gradient of image in both direction
print "sobel filter in use"
temp=cv2.subtract(temp,cv2.mean(temp))
score=[]
coor=[]
steps=16
print "steps size for scaning = %i"%steps
intervaly=imageA.shape[0]-20
for i in range(imageA.shape[1]-int(0.25*imageB.shape[1]),imageA.shape[1],steps):
for j in range(0,20,steps):
template=imageA[j:j+intervaly,i:i+intervalx] #template
if switch==1:
template = cv2.Laplacian(template,cv2.CV_32F)
if switch==0:
# print "using soble filter"
sobelx = cv2.Sobel(template,cv2.CV_32F,1,0,ksize=11)
sobely = cv2.Sobel(template,cv2.CV_32F,0,1,ksize=11)
template=sobelx+sobely#to get gradient of image
template=cv2.subtract(template,cv2.mean(template))
res=cv2.matchTemplate(temp,template,3)
_, val, _, loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)#val stores highest correlation from temp, loc stores coresponding starting location in temp
score.append(val)
coor.append(loc)
if(val > res_max):
res_max=val
xA1=i
yA1=j
xB1=loc[0]
yB1=loc[1]
print(val)
overlap=(1-float(xA1)/imageA.shape[1])
pointsA=[[xA1,yA1],[xA1+intervalx,yA1],[xA1,yA1+intervaly],[xA1+intervalx,yA1+intervaly]]
pointsB=[[xB1,yB1],[xB1+intervalx,yB1],[xB1,yB1+intervaly],[xB1+intervalx,yB1+intervaly]]
xB1=xB1*(1/fx)
yB1=yB1*(1/fx)
xA1=xA1*(1/fx)
yA1=yA1*(1/fx)
pointsA=[[xA1,yA1],[xA1+intervalx,yA1],[xA1,yA1+intervaly],[xA1+intervalx,yA1+intervaly]]
pointsB=[[xB1,yB1],[xB1+intervalx,yB1],[xB1,yB1+intervaly],[xB1+intervalx,yB1+intervaly]]
H,mask=cv2.findHomography(np.asarray(pointsB,float),np.asarray(pointsA,float),cv2.RANSAC,3)
return H,res_max
def rowStitch(imageA,imageB,fx,switch):
##################################################
# finding information between stiched row images #
##################################################
print " rowStitch function : finding homography"
res_max=-1
xA1=-1
yA1=-1
intervalx=16
intervaly=16
temp=imageB[:,:int(imageB.shape[1]*0.35)] #temp
if switch==1:
temp = cv2.Laplacian(temp,cv2.CV_32F)
if switch==0:
sobelx = cv2.Sobel(temp,cv2.CV_32F,1,0,ksize=11)
sobely = cv2.Sobel(temp,cv2.CV_32F,0,1,ksize=11)
temp=sobelx+sobely # to get gradient of image in both direction
temp=cv2.subtract(temp,cv2.mean(temp))
score=[]
coor=[]
steps=16
intervaly=imageA.shape[0]-100
for i in range(imageA.shape[1]-int(0.35*imageB.shape[1]),imageA.shape[1],steps):
for j in range(0,100,steps):
template=imageA[j:j+intervaly,i:i+intervalx] #template
if switch==1:
template = cv2.Laplacian(template,cv2.CV_32F)
if switch==0:
sobelx = cv2.Sobel(template,cv2.CV_32F,1,0,ksize=11)
sobely = cv2.Sobel(template,cv2.CV_32F,0,1,ksize=11)
template=sobelx+sobely#to get gradient of image
template=cv2.subtract(template,cv2.mean(template))
res=cv2.matchTemplate(temp,template,3)
_, val, _, loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)#val stores highest correlation from temp, loc stores coresponding starting location in temp
if(val > res_max):
res_max=val
xA1=i
yA1=j
xB1=loc[0]
yB1=loc[1]
print(val)
pointsA=[[xA1,yA1],[xA1+intervalx,yA1],[xA1,yA1+intervaly],[xA1+intervalx,yA1+intervaly]]
pointsB=[[xB1,yB1],[xB1+intervalx,yB1],[xB1,yB1+intervaly],[xB1+intervalx,yB1+intervaly]]
xB1=xB1*(1/fx)
yB1=yB1*(1/fx)
xA1=xA1*(1/fx)
yA1=yA1*(1/fx)
pointsA=[[xA1,yA1],[xA1+intervalx,yA1],[xA1,yA1+intervaly],[xA1+intervalx,yA1+intervaly]]
pointsB=[[xB1,yB1],[xB1+intervalx,yB1],[xB1,yB1+intervaly],[xB1+intervalx,yB1+intervaly]]
H,mask=cv2.findHomography(np.asarray(pointsB,float),np.asarray(pointsA,float),cv2.RANSAC,3)
return H,res_max
if __name__=="__main__":
########################################
# intializing parameters for stitching #
########################################
mypath='../CASE4A_1_focused'
# mypath='./images'
t1=time.time()
onlyfiles = [ f for f in listdir(mypath) if isfile(join(mypath,f)) ]
images = np.empty(len(onlyfiles), dtype=object)
onlyfiles.sort(key=lambda var:[int(x) if x.isdigit() else x for x in re.findall(r'[^0-9]|[0-9]+', var)])
onlyfiles=onlyfiles[10*156:]
##############
# PARAMETERS #
##############
row=2 # set number of rows
column=156 # set number of columns
fx=0.5 # set resizing factor for finding pairwise coordinates
x00,y00=0,0
output_size_x=column*10
output_size_y=row*10
coor=[]
score=[]
info=[]
r_overlap=int(round(0.35*640)) # row overlap information
c_overlap=int(round(0.25*480)) # column overlap information
for i in range(row):
row_1=[]
score.append([])
coor.append([])
files=onlyfiles[i*column:(i+1)*column]
if i%2==0:
files.reverse()
x,y=column*10,row*10
for j in range(column-1):
im1=cv2.imread( join(mypath,files[j]))
im2=cv2.imread( join(mypath,files[j+1]))
if j==0:
tile1 = pyvips.Image.new_from_file(join(mypath,files[j]), access="sequential")
bg = pyvips.Image.black(output_size_x,output_size_y)
tile1 = bg.merge(tile1, 'horizontal', -x, -y, mblend =False) #merging first image of each row with black mask to make coordinate system easier
coor[i].append([x,y])
tile2 = pyvips.Image.new_from_file(join(mypath,files[j+1]), access="sequential")
im1_s=cv2.resize(im1,None,fx=fx, fy=fx, interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA)
im2_s=cv2.resize(im2,None,fx=fx, fy=fx, interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA)
score[i].append(connect(im1_s,fx*r_overlap,fx*c_overlap)['bottom_score'])
H,val=Stitch(im1_s,im2_s,fx,0)
warped,im1_coor,im2_coor=warpImages(im1, im2, H)
# plt.imshow(warped)
# plt.show()
print im1_coor,im2_coor, "im1 coor"
x1,y1=im1_coor[2],im1_coor[0]
x2,y2=im2_coor[2],im2_coor[0]
print x,"xxxxx",x2,"xxxxx22222"
x=x+x2-x1
y=y+y2-y1
if y<0:
y=y2-y1
tile1 = tile1.merge(tile2, 'horizontal', -x, -y, mblend =False) # merging rest of the images in a row
coor[i].append([x,y])
score[i].append(connect(im2_s,fx*r_overlap,fx*c_overlap)['bottom_score'])
# tile1.write_to_file('tiles/images/tile1_%i.tiff'%i) #to save rows, stitched images of a row
if i>0:
print score,"score"
if i%2==1:
#finding index of best image in a row to match with corresponding row
r_index_1=score[i-1].index(max(score[i-1]))
r_index=score[i].index(max(score[i]))
else:
r_index_1=r_index
row_tile2=tile1
im1=cv2.imread( join(mypath,prior_files[r_index_1]))
im2=cv2.imread( join(mypath,files[r_index_1]))
im1=np.rot90(im1)
im2=np.rot90(im2)
im1_s=cv2.resize(im1,None,fx=fx, fy=fx, interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA)
im2_s=cv2.resize(im2,None,fx=fx, fy=fx, interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA)
H,val=rowStitch(im1_s,im2_s,fx,0) #finding homography
warped,im1_coor,im2_coor=warpImages(im1, im2, H) #finding coordinates
#calcualting coordinates
y1,x1=im1_coor[2],im1_coor[0]
y2,x2=im2_coor[2],im2_coor[0]
x_a,y_a=coor[i-1][r_index_1][0],coor[i-1][r_index_1][1]
x_b,y_b=coor[i][r_index_1][0],coor[i][r_index_1][1]
y_r=y00+y2
x_r=x00-x2+x1
y_r=y_a-(y_b-y_r)
x_r=x_a-(x_b-x_r)
print x_r,y_r,"vertical coordinates"
# for nn in range(len(coor[i])):
# coor[i][nn][0]=coor[i][nn][0]-x_r
info.append([x_r,y_r])
np.save("tiles/coor",info)
if i==1:
result= row_tile1.merge(row_tile2, 'vertical', -x_r, -y_r, mblend = False) #merging first and second row
else:
result= result.merge(row_tile2, 'vertical', -x_r, -y_r, mblend = False) #merging rest of the rows
x00,y00=x_r,y_r
# y00=y_r
prior_files=files
# print coor,"coordinates"
if i==0:
row_tile1=tile1
print "saving result"
result.write_to_file('result.tif')
print time.time()-t1, "time taken for stitching %i images"%(row*column)
To test this code change following parameters:
mypath = 'path of images'
row = number of rows
column =number of columns
r_overlap=int(round(0.35*640)) # 0.35 is the overlap in between each rows, 640 is the height of image
c_overlap=int(round(0.25*480)) # 0.25 is the overlap between pairwise images, 480 is the width of images
Change mypath,rows,column, images size
Issue Analytics
- State:
- Created 5 years ago
- Comments:8 (3 by maintainers)
 Top Results From Across the Web
Top Results From Across the Web
Big Data stitching - Image Analysis
Hi All, I have a bit of an issue in stitching lots of volumes together. I have tried to use the fiji stitcher...
Read more >Memory-efficient line stitching in very large images
First, we require that the rank and parent elements to both be pointer-sized, and aligned to 2*sizeof(pointer) in memory, for atomic CAS ...
Read more >How to stitch/view images in memory without building massive ...
I am working on a problem where I have 6 (or 10 at most) images from long screws and I want to stitch...
Read more >Exploiting Multi-Level Parallelism for Stitching Very Large ...
Since state-of-the-art microscopes coupled with chemical clearing procedures can generate 3D images whose size exceeds the Terabyte, ...
Read more >Image Stitching
Register images adjacently over time: The stitching will compute the shift between all images of all time-points, as well as of each image...
Read more > Top Related Medium Post
Top Related Medium Post
No results found
 Top Related StackOverflow Question
Top Related StackOverflow Question
No results found
 Troubleshoot Live Code
Troubleshoot Live Code
Lightrun enables developers to add logs, metrics and snapshots to live code - no restarts or redeploys required.
Start Free Top Related Reddit Thread
Top Related Reddit Thread
No results found
 Top Related Hackernoon Post
Top Related Hackernoon Post
No results found
 Top Related Tweet
Top Related Tweet
No results found
 Top Related Dev.to Post
Top Related Dev.to Post
No results found
 Top Related Hashnode Post
Top Related Hashnode Post
No results found

I made an experimental stitcher:
I can run it like this:
k2.jpgis a 1500 x 2000 pixel RGB JPG.The
VIPS_DISC_THRESHOLDenv var sets the point at which libvips flips between loading to memory and loading via a temp file: we need to save memory here, so we set the threshold low to make it decode the JPG images to temporary files in/tmp.CONCURRENCYsets the size of the libvips worker pool. Setting it to 1 saves memory for per-thread buffers, though it does make it run a little slower.PROGRESSmake it output some stuff as it runs, which is handy for debugging.So: I was able to blend 1600 images with merge on this machine into 54100 x 78020 pixel deepzoom pyramid in about 3m. With 64gb of memory, you should be able to join 80 x 80 images in about 12m, though it will vary a bit with image size.
To go higher, I think you’ll need to assemble your image in sections, sorry. Write each section out to a
.vfile to keep transparency (you’ll need a LOT of disc space), then do a second pass where you paste the sections together with more merge operators.Hello @jcupitt
I have tried to check where the code is taking maximum RAM. I am attaching massif file generated from valgrind https://github.com/KratosMultiphysics/Kratos/wiki/Checking-memory-usage-with-Valgrind. Please have a look on the massif file https://drive.google.com/file/d/1SCek6dNx521PMQolEa3vII8ufqRPcX4r/view?usp=sharing. The generated file is a result of stitching 156 column X 10 rows of images. I am attaching a screenshot of the massif visualizer. Here you can see function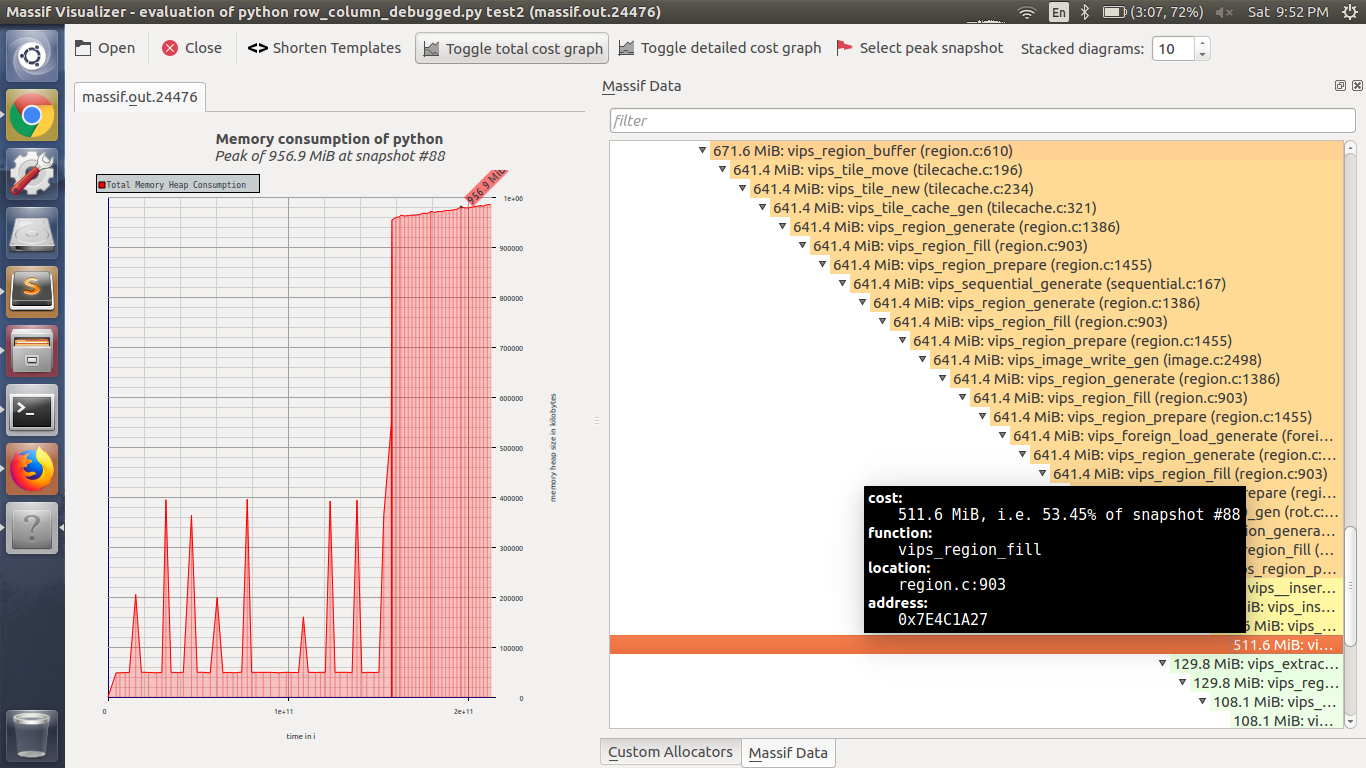
vips_region_fillis taking max RAM uses while saving the final tiff or dzi image result. Location- Region.c: 903In the python code I have just used only
joinfunction and the problem is a segmentation fault. RAM uses is less than Maximum RAM size <16 GB. Please give some suggestion to save the final result.