Nested commands: help not working
See original GitHub issueHi, I have some nested commands, this is my code:
#!/usr/bin/env node
/* eslint-disable @typescript-eslint/no-empty-function */
/* eslint-disable @typescript-eslint/no-misused-promises */
import 'module-alias/register';
import * as yargs from 'yargs';
import { virtualizeCan, VirtualizeCanOptions } from '@lib/modules/virtualizeCan';
import { simulateCan, SimulateCanOptions } from '@lib/modules/simulateCan';
import { simulateGps, SimulateGpsOptions } from '@lib/modules/simulateGps';
import { setTelemetryConfigPath, updateTelemetryGpsPort } from './utils';
yargs
.scriptName('eagle')
.command('virtualize', 'Virtualize a canbus interface', yargs => {
yargs
.command(
'can',
'Creates a can interface',
() => {},
async argv => {
const args: any = argv;
const canInterface = args.canInterface;
const options: VirtualizeCanOptions = {
silent: args.silent
};
await virtualizeCan(canInterface, options);
}
)
.demandCommand(1, 'You must specify the command "can"')
.options({
'can-interface': {
alias: 'i',
default: 'can0',
describe: 'The name of the can interface to create',
type: 'string'
},
'silent': {
alias: 's',
default: false,
describe: 'If logs will be displayed',
type: 'boolean'
}
}).argv;
})
.command('simulate', 'Simulate a canbus or a gps or both', yargs => {
yargs
.command(
'can',
'Simulates a canbus by sending messages from a log',
yargs => {
yargs.options({
'log': {
alias: 'l',
default: null,
describe: 'The log file that contains the messages to be sent over the can',
defaultDescription: 'There is a module built-in default can log if nothing is specified',
type: 'string'
},
'can-interface': {
alias: 'i',
default: 'can0',
describe: 'The name of the can interface to create',
type: 'string'
},
'silent': {
alias: 's',
default: false,
describe: 'If logs will be displayed',
type: 'boolean'
},
'simulate-time': {
alias: 't',
default: true,
describe: 'If the time of the can log will be simulated',
type: 'boolean'
},
'iterations': {
alias: 'n',
default: Infinity,
describe: 'The number of iterations in which the can log file will be sent to the canbus',
defaultDescription: 'If nothing is specified, the file is sent in an infinite loop',
type: 'number'
}
});
},
async argv => {
const args: any = argv;
const log = args.log;
const options: SimulateCanOptions = {
canInterface: args.canInterface,
silent: args.silent,
iterations: args.iterations,
simulateTime: args.simulateTime
};
await simulateCan(log, options);
}
)
.command(
'gps',
'Simulates a gps by sending messages from a log',
yargs => {
yargs.options({
'log': {
alias: 'l',
default: null,
describe: 'The log file that contains the messages to be sent over the gps',
defaultDescription: 'There is a module built-in default gps log if nothing is specified',
type: 'string'
},
'silent': {
alias: 's',
default: false,
describe: 'If logs will be displayed',
type: 'boolean'
},
'simulate-time': {
alias: 't',
default: true,
describe: 'If the time of the gps log will be simulated',
type: 'boolean'
},
'delay': {
alias: 'd',
default: 0,
describe:
'How many milliseconds will the gps simulator wait after opening the gps pseudoterminal port interface and before sending the messages over that interface',
type: 'number'
},
'iterations': {
alias: 'n',
default: Infinity,
describe: 'The number of iterations in which the gps log file will be simulated',
defaultDescription: 'If nothing is specified, the file is sent in an infinite loop',
type: 'number'
},
'keep-alive': {
alias: 'k',
default: false,
describe: 'Keep the process alive after having sent all the simulated gps data',
type: 'boolean'
},
'update-config': {
alias: 'u',
default: true,
describe:
'Updates the gps port on the config file of the telemetry to the same value of the opened gps interface. The config file is the one specified with the settings command.',
type: 'boolean'
}
});
},
async argv => {
const args: any = argv;
const updateConfig = args.updateConfig;
const log = args.log;
const options: SimulateGpsOptions = {
silent: args.silent,
iterations: args.iterations,
simulateTime: args.simulateTime,
delay: args.delay,
keepAlive: args.keepAlive
};
const gpsInstance = await simulateGps(log, options);
if (updateConfig) {
const gpsInterface = await gpsInstance.getGpsInterface();
updateTelemetryGpsPort(gpsInterface);
}
}
)
.command(
'all',
'Simulates both a canbus and a gps',
yargs => {
yargs.options({
'can-log': {
alias: 'c',
default: null,
describe: 'The log file that contains the messages to be sent over the can',
defaultDescription: 'There is a module built-in default can log if nothing is specified',
type: 'string'
},
'gps-log': {
alias: 'g',
default: null,
describe: 'The log file that contains the messages to be sent over the gps',
defaultDescription: 'There is a module built-in default gps log if nothing is specified',
type: 'string'
},
'can-interface': {
alias: 'i',
default: 'can0',
describe: 'The name of the can interface to create',
type: 'string'
},
'silent': {
alias: 's',
default: false,
describe: 'If logs will be displayed',
type: 'boolean'
},
'can-simulate-time': {
default: true,
describe: 'If the time of the can log will be simulated',
type: 'boolean'
},
'can-iterations': {
default: Infinity,
describe: 'The number of iterations in which the can log file will be sent to the canbus',
defaultDescription: 'If nothing is specified, the file is sent in an infinite loop',
type: 'number'
},
'gps-simulate-time': {
default: true,
describe: 'If the time of the gps log will be simulated',
type: 'boolean'
},
'delay': {
alias: 'd',
default: 0,
describe:
'How many milliseconds will the gps simulator wait after opening the gps pseudoterminal port interface and before sending the messages over that interface. Also the can will wait the same number of milliseconds before starting.',
type: 'number'
},
'gps-iterations': {
default: Infinity,
describe: 'The number of iterations in which the gps log file will be sent',
defaultDescription: 'If nothing is specified, the file is sent in an infinite loop',
type: 'number'
},
'gps-keep-alive': {
default: false,
describe: 'Keep the gps process alive after having sent all the simulated gps data',
type: 'boolean'
},
'gps-update-config': {
default: true,
describe:
'Updates the gps port on the config file of the telemetry to the same value of the opened gps interface. The config file is the one specified with the settings command.',
type: 'boolean'
}
});
},
async argv => {
const args: any = argv;
const gpsUpdateConfig = args.gpsUpdateConfig;
const canLog = args.canLog;
const gpsLog = args.gpsLog;
const canOptions: SimulateCanOptions = {
canInterface: args.canInterface,
silent: args.silent,
iterations: args.canIterations,
simulateTime: args.canSimulateTime
};
const gpsOptions: SimulateGpsOptions = {
silent: args.silent,
iterations: args.gpsIterations,
simulateTime: args.gpsSimulateTime,
delay: args.delay,
keepAlive: args.gpsKeepAlive
};
const [, gpsInstance] = await Promise.all([
new Promise(resolve =>
setTimeout(async () => resolve(await simulateCan(canLog, canOptions)), args.delay)
),
simulateGps(gpsLog, gpsOptions)
]);
if (gpsUpdateConfig) {
const gpsInterface = await gpsInstance.getGpsInterface();
updateTelemetryGpsPort(gpsInterface);
}
}
)
.demandCommand(
1,
'You must use "can", "gps" or "all" command. To see all options of a command use the -h flag.'
).argv;
})
.command(
'settings',
'Change the settings of the module',
yargs => {
yargs.options({
'telemetry-config-path': {
alias: 't',
demandOption: true,
describe:
'The path to the telemetry config file. It will be updated automatically when calling the gps simulator with the option --update-config set to true. Use "null" to set it to null.',
type: 'string'
}
}).argv;
},
argv => {
const args: any = argv;
const telemetryConfigPath = args.telemetryConfigPath === 'null' ? null : args.telemetryConfigPath;
setTelemetryConfigPath(telemetryConfigPath);
}
)
.demandCommand(1, 'You must use either virtualize of simulate command')
.epilogue(
'For more information, find our manual at https://github.com/eagletrt/eagletrt-telemetria-simulator#readme'
).argv;
If I then do something like eagle virtualize can --help it is ok.
If I do eagle simulate --help, I get:
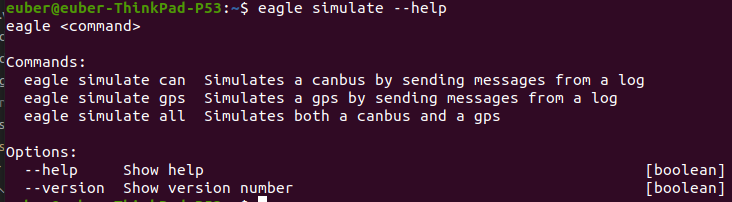
And this is ok, too.
But if i do eagle simulate can --help, I get only:
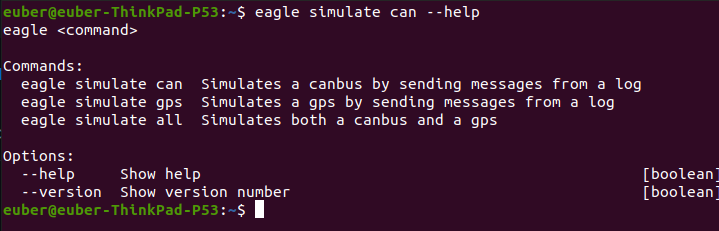
Which is exactly the same result of the one above, without getting the options of eagle simulate can.
If I then add .help('h') , such as:
.command('simulate', 'Simulate a canbus or a gps or both', yargs => {
yargs
.command(
'can',
'Simulates a canbus by sending messages from a log',
yargs => {
yargs
.options({
'log': {
alias: 'l',
default: null,
describe: 'The log file that contains the messages to be sent over the can',
defaultDescription:
'There is a module built-in default can log if nothing is specified',
type: 'string'
},
'can-interface': {
alias: 'i',
default: 'can0',
describe: 'The name of the can interface to create',
type: 'string'
},
'silent': {
alias: 's',
default: false,
describe: 'If logs will be displayed',
type: 'boolean'
},
'simulate-time': {
alias: 't',
default: true,
describe: 'If the time of the can log will be simulated',
type: 'boolean'
},
'iterations': {
alias: 'n',
default: Infinity,
describe:
'The number of iterations in which the can log file will be sent to the canbus',
defaultDescription: 'If nothing is specified, the file is sent in an infinite loop',
type: 'number'
}
})
.help('h');
},
async argv => {
const args: any = argv;
const log = args.log;
const options: SimulateCanOptions = {
canInterface: args.canInterface,
silent: args.silent,
iterations: args.iterations,
simulateTime: args.simulateTime
};
await simulateCan(log, options);
}
)
.demandCommand(
1,
'You must use "can", "gps" or "all" command. To see all options of a command use the -h flag.'
).argv;
})
And I do eagle simulate can -h, it works:
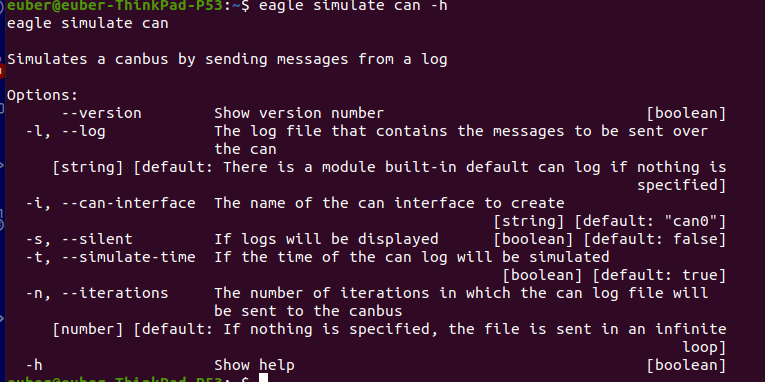
Issue Analytics
- State:
- Created 2 years ago
- Comments:6 (2 by maintainers)
 Top Results From Across the Web
Top Results From Across the Web
Nested commands and help using click - Stack Overflow
I'm trying to figure out the latter. When running foo.py sync , then implicitly, the global options are impacting the behavior of sync...
Read more >Can't make nested subcommands work · Issue #161 - GitHub
I'm trying to use nested commands, where the "first layer" subcommand has no flag/options but is just a bridge for its subcommands: CLI::App ......
Read more >Commands and Groups — Click Documentation (7.x)
Commands and Groups¶. The most important feature of Click is the concept of arbitrarily nesting command line utilities. This is implemented through the ......
Read more >A guide to bash commands redirecting, chaining, and nesting
Once you have some basic practical knowledge of how to use shell commands, you kind of start to lean towards saving some time...
Read more >Commands and Groups - click
The most important feature of click is the concept of arbitrarily nesting command line utilities. This is implemented through the Command and Group ......
Read more > Top Related Medium Post
Top Related Medium Post
No results found
 Top Related StackOverflow Question
Top Related StackOverflow Question
No results found
 Troubleshoot Live Code
Troubleshoot Live Code
Lightrun enables developers to add logs, metrics and snapshots to live code - no restarts or redeploys required.
Start Free Top Related Reddit Thread
Top Related Reddit Thread
No results found
 Top Related Hackernoon Post
Top Related Hackernoon Post
No results found
 Top Related Tweet
Top Related Tweet
No results found
 Top Related Dev.to Post
Top Related Dev.to Post
No results found
 Top Related Hashnode Post
Top Related Hashnode Post
No results found

Thank you.
I don’t know, I think it could be added to the examples, in something called like “subcommands something”, pointing out that argv should be only in the end.
@euberdeveloper, I see the problem, in the
builderfunctions, you don’t want to call.argv(you only call this once at the top level). This works like a charm for me:Can you think of a place in the docs where we could call this out?